Blinded Sample Size Reestimation in Clinical Trials with Recurrent Event Data and Time-dependent Event Rates
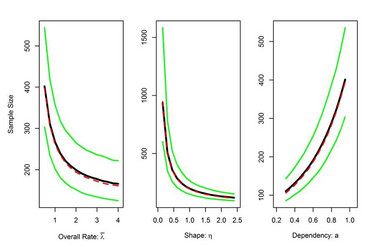
The determination of the number of patients to be included in a clinical study is a key aspect of the study's design. However, the risk of sizing the study inappropriately is often considerable due to uncertain a priori information on variances or event rates. To overcome this problem so-called internal pilot studies have been proposed which allow to reestimate the required sample size during the course of the study based on accruing data. If the interim sample size adjustment is done without breaking the treatment code in blinded, randomized trials, then the procedure is called blinded sample size reestimation (BSSR).
This project considered such adaptive designs for recurrent events and aimed to (a) systematically compare existing BSSR methods for recurrent event data; (b) extend existing methodologies to include covariates such as baseline disease severity and intermittent missingness patterns; (c) develop statistical methodology for recurrent events with time-varying rates; and (d) explore the feasibility of applying these methodologies to multi-regional and multi-national trials with complex recruitment schemes.
The project was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG).
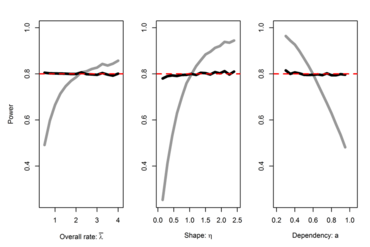
In planning a clinical trial the determination of the number of patients to be included in the study is a key aspect of the design since the sample size has direct implications on costs, duration and feasibility. However, a priori information on the size of nuisance parameters such as within-group variances and overall (or placebo control) rates is often very vague since data are only available from small-scale early phase studies and/ or studies that differ in various design aspects (e.g. definition of endpoints, mono vs. multi-centre studies). Therefore the risk to size a study inappropriately is often substantial. To overcome this problem the use of so-called internal pilot study designs for clinical trials was proposed. These allow to reestimate the required sample size during the course of the study based on accruing data (Wittes and Brittain 1990). The interim sample size adjustment can be carried out with or without breaking the treatment code during the ongoing trial (Friede and Kieser 2001).
The advantages of the blinded procedures over unblinded ones are that they, in contrast to unblinded procedures, preserve the integrity of the trial without the need of a Data Monitoring Committee (DMC) and that they have a smaller impact on the type I error rates of hypothesis tests (Kieser and Friede 2003). For these reasons blinded sample size reestimation procedures (BSSR) are generally favoured over unblinded procedures by regulatory authorities (CHMP 2007; FDA 2010).
Aims
This project aimed to
- systematically compare existing methods for blinded sample size reestimation (BSSR) with recurrent event data.
- extend existing methodologies to include covariates such as baseline disease severity.
- explore the modelling of random effects and how they can be detected.
- develop statistical methodology for BSSR with recurrent-event data with time-varying rates.
- extend BSSR methodologies to use information on intermittent missingness.
- study explained variation as a new concept for sample size estimation and reestimation.
- explore the feasibility of applying these methodologies to multi-regional and multi-national trials with complex recruitment schemes.
Events and Publications
The last annual project meeting on blinded sample size reestimation in clinical trials took place in 2016 on November 9th in the Heyne House of the University Göttingen. (Program - Symposium)
- Asendorf T, Henderson R, Schmidli H, & Friede T (2019). Modelling and sample size reestimation for longitudinal count data with incomplete follow up. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 28(1), 117–133. [Full text]
- Mütze T, Munk A, Friede T (2016) Design and analysis of three-arm trials with negative binomially distributed endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 35: 505-521. Abstract
- Alotaibi R, Fiaccone R, Henderson R, Stare J (2015) Explained variation for recurrent event data. Biometrical Journal 4: 571-591. Abstract
- Schneider S, Schmidli H, Friede T (2013) Blinded sample size reestimation for recurrent event data with time trends. Statistics in Medicine 32: 5448-5457. Abstract
- Schneider S, Schmidli H, Friede T (2013) Robustness of methods for blinded sample size reestimation with overdispersed count data. Statistics in Medicine 32: 3623-3635. Abstract
- Schneider S, Schmidli H, Friede T (2013) Blinded and unblinded internal pilot study designs for clinical trials with count data. Biometrical Journal 55:617-633 Abstract
PhD thesis
- Schneider, Simon (2014) - Dissertation: Verblindete Fallzahlanpassung in klinischen Studien mit Ereigniszähldaten Dissertation, University Mannheim
Software
- R-Package: Study Planning and Adaption of Sample Size SPASS
Presentations
- Health – Exploring Complexity (HEC) in München (2016): Sample size (re-) estimation for recurrent event data based on the explained variation. (Speaker: Antonia Zapf)
- AG Adaptive Designs in Padua, Italien (2016): Blinded sample size reestimation for time dependent negative binomial counts with incomplete follow up. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Deutsche Arbeitsgemeinschaft Statistik – Tagung in Göttingen (2016): Blinded sample size reestimation for time dependent negative binomial counts. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Biometrisches Kolloquium in Dortmund (2015): Blinded sample size reestimation for time dependent negative binomial observations. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Adaptive Design Workshop in Köln (2015): Blinded sample size reestimation for time dependent negative binomial observations. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Oberseminar am Institut für Medizinische Statistik der UMG in Göttingen (2014): Developing data products with R Shiny. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- AG Adaptive Designs in Basel, Schweiz (2014): Sample size reestimation for poisson counts in randomized controlled clinical trials. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Informatik, Biometrie und Epidemiologie – Tagung in Lübeck (2013): Sample size reassessment strategies for recurrent event data with time trends. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)
- Internal Society for Clinical Biostatistics - Tagung in München (2013): Adaptive Designs using sample size reassessment strategies for recurrent event data with time trends. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)
- Deutsche Arbeitsgemeinschaft Statistik – Tagung in Freiburg (2013): Blinded sample size reestimation for recurrent event data with time trends. (Speaker: Thomas Asendorf)
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Informatik, Biometrie und Epidemiologie – Tagung in Braunschweig (2012): Blinded and unblinded internal pilot study designs for clinical trials with overdispersed count data. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)
- Adaptive Designs and Multiple Testing Procedures in Heidelberg (2012): Blinded and unblinded internal pilot study designs for clinical trials with overdispersed count data. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)
- Internal Society for Clinical Biostatistics - Tagung in Bergen, Norwegen (2012): Blinded and unblinded internal pilot study designs for clinical trials with overdispersed count data. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)
- 58. Biometrisches Kolloquium in Berlin (2012): Robustheit verschiedener Ansätze zur verblindeten Fallzahlanpassung für klinische Studien mit Zähldaten. (Speaker: Simon Schneider)